Our publications
Resources produced during our past projects are accessible here.
For more than 10 years, we have capitalised documents on groundwater development, irrigation, drinking water supply and sanitation. You can find lessons learnt from the field, project reports, technical sheets, (training) manuals, videos, etc.
Check out and share the information you are interested in with the rest of the sector in order to support local enterprises and strengthen their technical and business skills.
Study on the development potential of solar irrigation in the Maradi region – Niger
Study of the Djirataoua I irrigation scheme to assess the relevance and feasibility of implementing solar-powered irrigation. The report highlights both the strong points and points of attention for the implementation of solar irrigation in the Djirataoua I AHA, along with a roadmap of actions to be carried out.
Farmer-led climate smart irrigation – infosheet
The gap between (solar) irrigation technologies and smallholders is reducing in Africa and Asia. However, a lack of know-how and practical skills in technical, commercial, and financial aspects, or misconceptions about the benefits of tailor-made irrigation solutions, becomes an obstacle to the sector’s development. Practica’s approach aims to lead the development of climate-smart and solar-powered irrigation in the most sustainable direction. This brochure explains how.
PuPu pump information sheet
Technical information over the PuPu pump. Developed by Practica, this pump can pump sludge of different consistencies into a tank away from the emptied pit. It suits densely populated areas that are difficult to access by vacuum trucks.
The PuPu pump is now commercialised in West Africa by Energy & Services.
More information on this technology is available on the website www.pupu-pump.com including technical information, videos and contacts.
Volterra – infosheet
Geophysical siting is an important part of water point construction. It prevents money and labor being wasted into drilling failed boreholes. While traditional VES equipment supports siting at a limited scale, it is too expensive and sparsely available in the global rural South. Practica therefore developed the Volterra, a device which is ~8 times cheaper than traditional equipment, but with the same borehole success rate.
TokenTap – infosheet
The TokenTap is a mechanical prepaid water device fit for rural settings. Prepaid water technologies are essential tools for fair, transparent and reliable revenue collection. They contribute to the sustainable management of water supply assets. For prepaid water systems to work in rural settings, the hardware must be reliable, robust, and easy to install and maintain for anyone with a basic technical skillset. Additionally, it should come at low operational costs. Practica developed the TokenTap to meet these conditions. The TokenTap is particularly user-friendly, easy to install, and operate. Additionally, it offers critical functionalities including a tracking device and a web dashboard to monitor water sales.
WaterTime – Infosheet
WaterTime is a modular asset-focused set-up and business approach to managing small-scale piped drinking water systems sustainably. Its objective is to increase reliable access to basic water supply for people in underserved areas by offering a more sustainable alternative to commonly used handpumps.
Zainer – infosheet
Due to climate change, rainfall patterns in Africa have become less predictable. As a result, African farmers experience production loss for their main rain-fed staple crops. Especially for smallholders, this poses a serious risk for food security and family income. Affordable mechanization of climate-smart agricultural practices can overcome the drawbacks. Practica, therefore, initiated the development of a simple tool to quickly and cheaply produce small basins or pits for local rainwater retention. We have named this tool ‘Zaïner’, as a reference to the traditional West African practice of producing small plantholes, called Zaï.
The Drillers Toolbox brochure
The Drillers Toolbox is an application for borehole data management, including modules for drill logs, pump tests and vertical electrical soundings (VES).
This document is available in English, French and Portuguese.
Practica at a glance
Practica’s organisational profile presenting our main portfolios: Irrigation, Water Supply, Sanitation and Groundwater Development. This one page highlights for each portfolio the main innovations Practica works on. For more information browse our website or contact us at: info@practica.org
Water System Asset Management: overview of practices and tools
Water Systems Asset Management (WSAM) aims to support the strategic shift in water systems operation and maintenance: transitioning from a reactive approach of problem-solving once downtime occurs to a proactive strategy focused on prevention and mitigation. Practica has employed academic consultancy team (ACT) to better understand the advantages and disadvantages of various asset management approaches, practices and tools. On the basis of desktop research and interviewing 11 different WASH organisations (combi of public, NGO, social entrepreneurs) working in the global South with various tools, a comparison was made and number of recommendations have been formulated. The report shows the diversity in WSAM interpretations, and the practices and tools in use. It calls for the water sector to converge on the impact to be delivered and the type of results to be shared on WSAM. To know more about Practica’s experience and WSAM tools, see: https://www.practica.org/our-innovations/asset-management-water-systems/
Training guide on the financial aspects of solar irrigation systems
This is a practical training guide on the financial related aspects of small-scale solar irrigation. It provides a theoretical base on the most relevant concepts and space to practice these concepts with help of calculations and case studies. It aims to be a practical guide for credit officers, development partners and finance trainers.
Asset management and monitoring manual
This document is available in English and Portuguese.
Asset management is an approach to optimize the use of an asset – and to assure that the service level meets the needs of the user. It is one – of multiple – critical elements to ensure a technically and financially sustainable water system.
It can be used to:
• record the asset and make a maintenance plan for it – to ensure technical sustainability;
• use it for financial prognosis – and analyze the financial sustainability of it;
• optimize the asset plan by finding the optimum between financial and technical sustainability in relation to the service level;
• monitor the asset to ensure one can avoid breakdowns due to mismanagement.
The objective of this manual is to gain a general understanding of the principles of asset management and how one can apply it to a piped water system.
Solar Irrigation Training Brochure
This brochure gives an overview of our practical trainings that we developed to give a basic understanding of the technical and financial aspects of solar irrigation systems.
Adopting asset management tools to model cost recovery of rural piped water services
This policy paper is the result of a piped water project in Northern Uganda implemented under the Dutch WASH SDG Programme and partners of the WASH Alliance International. The policy paper responds to the ambition of the Government of Uganda to supply all households with piped water by 2040. To realise a sustainable acceleration of piped water services, it is essential that recurrent costs are recovered. Cost recovery through water pricing remains, however, a controversial and politically challenging topic.
Asset management for water systems
Water Systems’ Asset Management is an approach to support water users’ committees, water operators, caretakers, and governmental institutions in optimising their water systems’ technical and financial performance.
It assures the water quantity & quality, and systems’ reliability and accessibility, it matches customers’ demand, and it supports decisions on infrastructure’s design, use and maintenance.
Market-Based Sanitation Strategies Using a GIS
This learning note presents the main ideas behind a basic approach to using a geographic information system (GIS) to establish geographic segmentation as part of a market-based sanitation (MBS) strategy. The use of GIS assumes that the most densely populated, most accessible zones are characterized by a more dynamic economy, making them easier to tap into to develop a sanitation market that is currently nonexistent or, at best, barely exists. A GIS facilitates the task of differentiating those dynamic, accessible zones, allowing partners to target their interventions more accurately and prioritize their actions.
All of the tools and data sources presented here are open-source and accessible, including for people who have no prior experience with GIS.
More information and additional learning briefs are available here.
How to assess the size of a sanitation market and segment It?
Any market-based intervention must be based on a good understanding of the size and characteristics of the potential market for various products and services in the target areas. This information helps to prioritize activities, define sales and marketing systems that are appropriate for different market segments, and help service providers understand the size and nature of the market opportunity.
Ultimately, showing the market size and its characteristics will also help stimulate public and private investments in the sanitation sector toward the products most likely to contribute to the sustainable economic viability of the sanitation market.
More information and additional learning briefs are available here.
Human Centered Design for sanitation products
This document provides guidance on the skills, steps, and resources needed to conduct a rapid human-centered design (HCD) process for improved toilet products in rural areas. The lessons and tips shared are based on work done as part of a broader sanitation market development exercise in the Maradi and Zinder regions of Niger.
HCD is a process for understanding people’s needs, preferences, and behaviors to enable working with them
to implement the sustainable solutions they value. Using the HCD approach to develop product options allows incorporation of ideas and feedback directly from the people who need improved sanitation solutions to ensure that the final products will meet both the needs and preferences of potential customers. This is especially important when using a market-based approach, as people will be asked to spend their own money on toilets.
More information and additional learning briefs are available here.
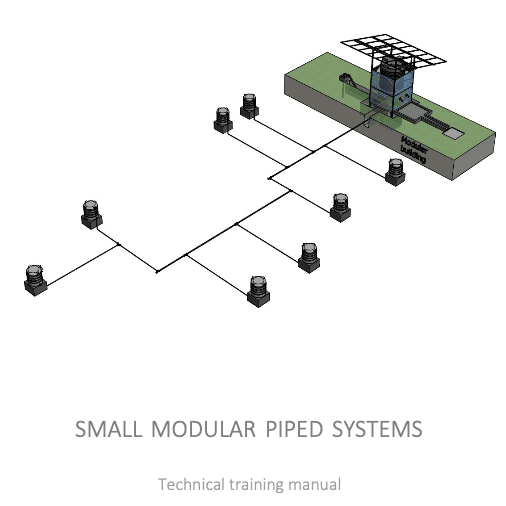
Small modular and solar piped water systems
The purpose of this training manual is to serve as reading material and background information for a training about the technical aspects of modular solar drinking water supply systems.
Three types of trainings are also part of the training package. 1) To understand the design and rationale of modular piped systems and how design decisions affect the operational expenses; 2) about the business case and asset management behind the concept. This training gives tools and insights on how one can maintain and financially monitor the system; 3) a technical hands-on field training on construction, installation and maintenance of modular systems.
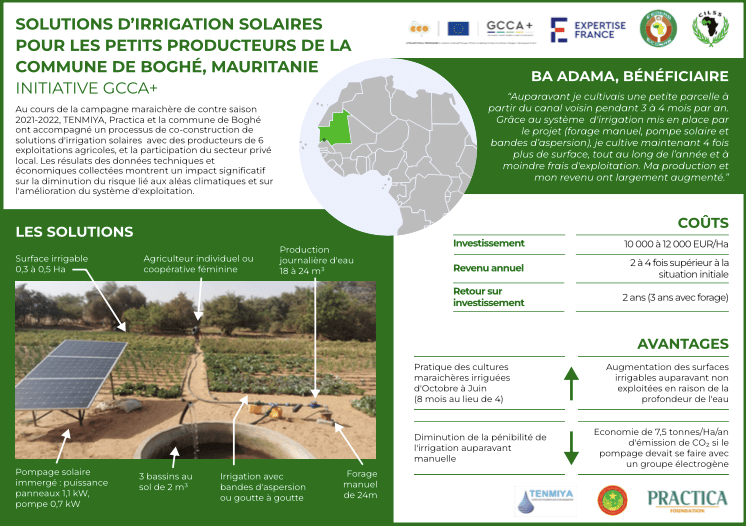
Technical reference solar irrigation solutions
As part of the project GCCA+ financed by the European Union and implemented by Expertise France we implemented a pilot on the “Co-construction of innovative solar irrigation solutions” in the town of Boghé, in Mauritania. Based on the result that we obtained after co-constructing the solutions with the local farmers, we developed these technical reference to be used as an example and guideline when setting up solar irrigation systems.